Eye Cancer – Eye Uveal Melanoma
Eye Cancer Treatment
Uveal Melanoma is a type of Eye Cancer that develops in cells that produce melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color. your eyes too has melanin-producing cells and candevelop melanoma. Eye melanoma is also called Ocular Melanoma.
Most eye melanomas occur in the part of the eye that you cannot see when you look in the mirror. This makes eye melanoma difficult to detect. In addition, eye melanoma does not typically cause any early signs or symptoms.
Treatment is available for eye melanomas. Treatment of some small eye melanomas may not affect your vision. However, treatment of large eye melanomas typically results in some vision loss.
Eye Cancer Symptoms:
Especially, Eye Cancer may not cause signs and symptoms. When they do occur, signs and symptoms of eye melanoma can include:
- A feeling of glare or dust spots in your vision (flyers).
- A dark spot growing on the iris.
- A change in the shape of the dark circle (pupil) in the middle of your eye.
- Weak or blurred vision in one eye.
- Peripheral vision loss.
When to see a doctor:
Make an appointment with our expert eye surgeon if you have any signs or symptoms that worries you. Sudden changes in your vision indicate an emergency, so contact our eye surgeon immediately.
Eye Cancer Reasons:
Particularly, it is not clear what causes eye melanoma. As a result of research, it is known that Eye Cancer occurs when errors occur in the DNA of healthy eye cells. DNA errors cause cells to grow and multiply out of control, so mutated cells continue to live when they would normally die. Also, the mutated cells accumulate in the eye and form an eye melanoma.
Where Eye Cancer occurs:
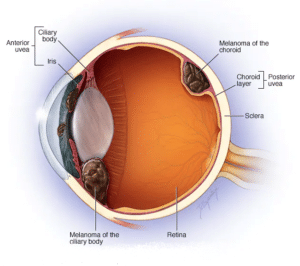
Especially, eye melanoma most often develops in cells in the middle layer of your eye (uvea).
There are three parts of the uvea, and each can be affected by eye melanoma:
- Iris, the colored part at the front of the eye.
- The choroid layer, which is the layer of blood vessels and connective tissue between the sclera and retina behind the uvea.
- The ciliary body located in the anterior part of the uvea and secretes the transparent fluid (watery humor) into the eye.
Also, eye melanoma can occur in the outermost layer of the eye (conjunctiva), the socket surrounding the eyeball, and the eyelid, but this type of eye melanoma is very rare.
Risk factors:
Risk factors for primary melanoma of the eye include:
- People with light eyes: People with blue eyes or green eyes have a higher risk of eye melanoma.
- In those with white skin: People with white skin have a higher risk of eye melanoma than people of other races.
- Age factor: The risk of eye melanoma increases with age.
For those with certain inherited skin disorders: A condition call dysplastic nevus syndrome, which causes abnormal moles, can increase your risk of developing melanoma on your skin and eyes.
Additionally, people with abnormal skin pigmentation involving the eyelids and adjacent tissues and increase pigmentation in their uveas (known as ocular melanocytosis) are also at increase risk of developing eye melanoma.
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light
Although, the role of ultraviolet exposure in eye melanoma is unclear. There is some evidence that exposure to UV light, such as light from the sun or tanning beds, may increase the risk of eye melanoma.
Certain genetic mutations
Especially, certain genes passes from parents to children can increase the risk of eye melanoma.
Complications of eye melanoma can include:
Increased pressure inside the eye (glaucoma). An enlarged eye melanoma can cause glaucoma. Therefore, glaucoma signs and symptoms may include eye pain and redness, as well as blurred vision and vision loss. Large eye melanomas often cause vision loss in the affected eye and can cause complications such as retinal detachment that also cause vision loss.
On the other hand, small eye melanomas can cause some loss of vision if they occur in critical areas of the eye. You may have trouble seeing the center or the side of your vision. Also, very advance eye melanomas can cause complete vision loss.
Moreover, eye melanoma that spreads beyond the eye. Eye melanoma can spread outside the eye and to distant parts of the body, including the liver, lungs, and bones.
Diagnosed:
To diagnose eye melanoma, your doctor may recommend:
- Eye tests: our doctor will examine the outside of your eye and look for enlarged blood vessels that could indicate a tumor inside your eye. Then, with the help of instruments, our doctor will look into your eyes.
- Examination with binocular indirect ophthalmoscopy: Our eye surgeon will examine your eye with an ophthalmoscope.
- Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy examination: Our doctor will examine the inside of your eye with a biomicroscope with a high light source.
- Eye ultrasound: An eye ultrasound will test with a device that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of your eye.
- Visualization of the blood vessels in and around the tumor (angiogram): During an angiogram of your eye, a colored dye is inject into a vein in your arm. The dye travels to the blood vessels in your eyes. A camera with special filters to detect paint takes photos with a flash every few seconds for several minutes.
- Optical coherence tomography OCT Imaging test: Pictures of the uveal tract and retinal sections are create with the OCT device.
- Removal of suspicious tissue sample for testing. In some cases, our doctor may recommend a procedure to take a tissue sample (biopsy) from your eye. Particularly, a thin needle is inserted into your eye to remove the sample and used to remove suspicious tissue. Accordingly, the tissue will be test in a lab to determine if it contains eye melanoma cells. Although, an eye biopsy is not usually necessary to diagnose eye melanoma.
Determining whether the cancer has spread:
Especially, our doctor may recommend additional tests and procedures to determine if the melanoma has spread (metastasized) to other parts of your body.
Other tests:
- blood tests to measure liver function.
- chest x-ray.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan.
- Abdominal ultrasound.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
Treatment:
Especially, your Eye Cancer treatment options will depend on the location and size of the eye melanoma, as well as your overall health and preferences.
Treating small eye melanomas:
Particularly, a small eye melanoma may not require immediate treatment. If the melanoma is small and not growing, you and our doctor may prefer to wait and watch for signs of growth.
Meanwhile, if the melanoma grows or causes complications, then you may choose to seek treatment.
Radiation therapy:
Especially, radiation therapy uses high-powered energy, such as protons or gamma rays, to kill cancer cells. Therefore, radiation therapy is typically use for small to medium-sized eye melanomas.
Usually, radiation is deliver to the tumor by placing a radioactive plaque in your eye directly over the tumor in a procedure called brachytherapy. Also, the plaque is hold in place with temporary sutures. Additionally, this plaque to be place in your eye is similar to a bottle cap and contains low radioactive particles. Therefore, It stays in place for four to five days before it is remove.
Also, the radiation can come from a machine that directs radiation, such as proton beams, into your eyes (external beam radiation or teletherapy). This type of radiation therapy is usually monitor and manage over several days.
Laser therapy:
Especially, laser treatments to kill melanoma cells may be an option in some cases. One type of laser therapy, call thermotherapy, uses an infrared laser and is sometimes use in conjunction with radiation therapy.
Photodynamic therapy:
Photodynamic therapy combines drugs use for this treatment with a specific wavelength of light. Therefore, the drug makes cancer cells vulnerable to light. The treatment damages the vessels and cells that make up the eye melanoma. Especially, photodynamic therapy is use for smaller tumors as it is not effective for larger cancers.
Cold treatments:
For some small eye melanomas, extreme cold (cryotherapy) may be use for destroy the melanoma cells. However, this treatment is not commonly use.
Surgery:
Operations used to treat eye melanoma include procedures to remove part of the eye or the procedure to remove the entire eye. Which procedure to perform depends on the size and location of your eye melanoma.
Options may include:
Surgery to remove melanoma and a small area of healthy tissue. Alsu operation to remove the melanoma and the band of healthy tissue surrounding. it may be an option to treat small melanomas.
Especially, surgery to remove the entire eye (enucleation). Enucleation is often use for large eye tumors. It can also be use if the tumor is causing eye pain.
After the melanoma eye is remove, an implant is place in the same position and the muscles that control the movement of the eye are attached to the implant, allowing the implant to move.
After you have had some time to heal, an artificial eye (prosthesis) is ready. The front surface of your new eye is custom made and painted to match your existing eye.
Useful Links
What is Prosthetic Eye Surgery – Enucleation. Vitrectomy Surgeries. About Keratoplasty Surgery What is the cost of eye cancer treatments. Strabismus Crossed Eye Squint Treatments, Diabetic Retinopathy Disease. Macular Degeneration Treatments. Glaucoma Disease and Treatments. Retinitis Pigmentosa Disease and Treatments. Dry Eye Syndrome Treatments. Periodic Eye Examinations.
Your Expert Eye Surgeons

Education Information:
He completed his primary, secondary and high school education in Ankara. Fevzi Senturk graduated from Ankara University Faculty of Medicine with a degree in 1994, and subsequently received his Ophthalmology Specialization training from Eskisehir Osmangazi University Faculty of Medicine in 2000. Afterwards, Fevzi Senturk completed his Retina Fellowship at Istanbul Retina Institute and earned the title of Associate Professor at this institution. He is still continuing his academic career by taking the title of Professor at Istanbul Medipol University. He has focused his scientific and clinical studies on retinal diseases, Vitreoretinal surgery and cataract surgery.Awards,Memberships and Scientific Research:
- Retinal capillary hemangioma: AB interno surgical excision, 43rd National Congress Awards, Best Video First Prize, 2009
- Photodynamic therapy guided by indocyanine green angiography in chronic central serous chorioretinopathy, Turkish Journal of Ophthalmology, Best Publication Third Prize, 2000
- Retinal capillary hemangioma: AB interno surgical excision, 43rd National Congress Awards, Best Video First Prize, 2009
- Photodynamic therapy guided by indocyanine green angiography in chronic central serous chorioretinopathy, Turkish Journal of Ophthalmology, Best Publication Third Prize, 2000
- Vitreoretinal Surgery Techniques, Second Edition, Hayat Medicine Bookstore, 2008
- Eye Diseases and Anti-VEGF Therapy 2010.
- Ocular Electrophysiology (TOD Education Publications No 13) Meaning of VEP, VEP registration and parameters in ISCEV standards., 2011
- Clinical Eye Atlas (Oxford Atlases in Ophthalmology), 2012
- Imaging in Ophthalmology, Microperimetry, 2013
- Ocular Electrophysiology (TOD Education Publications 1st Edition), Multifocal Electroretinogram Recording and Evaluation, 2022.
- Current Vitreoretinal Surgery (TOD Education Publications), Surgical Anatomy of the Retinal and Vitreous, 2022.
- Turkish Medical Association
- Turkish Ophthalmology Association
- Turkic Republics Ophthalmology Association
- Electrodiagnostic unit board membership
- Electrodiagnostic unit training representative
- International Society for Clinical Electrophysiology of Vision (ISCEV)
Specialized Treatments and Surgeries:
- Macular Degeneration Disease and Treatments
- Retinal Detachment Treatments
- Retinal Hemorrhages Due to Diabetes and Hypertension and Their Treatments
- Retinitis Pigmentosa Treatments
- Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
- Retinal Vascular Occlusions
- Epirentinal Membrane
- Macular Hole
- Glaucoma eye pressure
- Neuroophthalmological Diseases
- Vitrectomy-Retina Surgery
- Intravitreal Injection Treatments
- Argon Laser Photocoagulation Treatment
- Photodynamic Therapies
Foreign language:
- English
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY of Ankara
28 Years of Experience
>25.000 Surgery
Definitely avoid low-cost Eye Treatments
You may think that a cheap eye treatment is right for you. This might be fine if you're buying a cheap TV, but it's not worth the gamble with your eyesight. But as you know, having cheap eye surgery means sacrificing technology, physician quality, medical care and sterile conditions, and most importantly, taking risks. The issues that fall on a patient who wants to have cataract surgery and should pay the most attention; The hospital with the latest technology in cataract surgery and imaging devices, a sterile environment, and an experienced doctor and clinical team should be selected. We would like to remind all our patients that they only have two eyes and that the most important and most sensitive sense organ is their eyes.
None of these things are more important than your eye health, and we do not compromise on quality and cutting-edge technology. We offer you our prices in a very understandable, fair and affordable way.
There are no hidden costs in our pricing. We make eye treatment affordable for you.